Union Budget 2024-25: Transformative Initiatives for a Prosperous India

Union Budget 2024-25: Major Allocations and Reforms Unveiled
The Union Budget 2024-25 has been announced, bringing forth a series of transformative measures aimed at bolstering the country’s infrastructure, social welfare, and economic growth. This budget reflects the government’s commitment to inclusive development, with substantial allocations and strategic initiatives across various sectors.
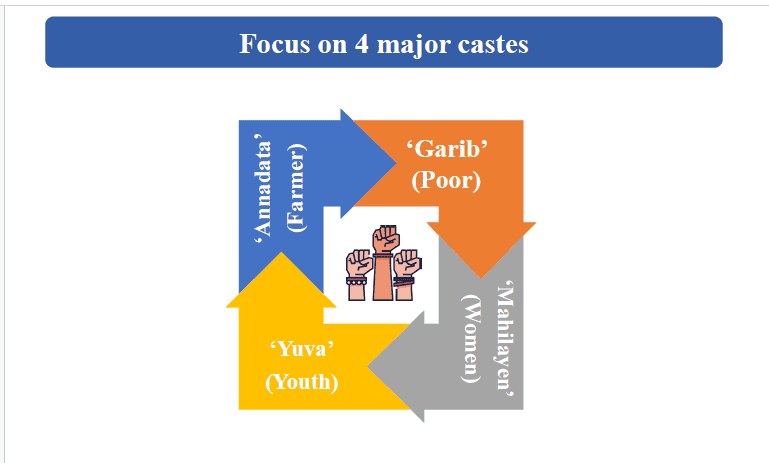
Major Allocations and Projects
Bihar Highways Development: The budget allocates a significant ₹26,000 crore for the development of highways in Bihar. This substantial investment aims to improve connectivity, boost economic activities, and enhance the overall infrastructure of the region. With better roads, the state is expected to witness a surge in trade and tourism, creating new opportunities for its residents.
Capital Development in Andhra Pradesh: An allocation of ₹15,000 crore has been made for the development of Andhra Pradesh’s capital. This fund will be arranged within the current fiscal year, signaling a strong focus on urban development and modernization of the state’s administrative hub.
Schemes for Women and Girls: In a landmark move, ₹3 lakh crore has been allocated to schemes benefiting women and girls. This initiative aims to empower women through various welfare programs, ensuring their safety, education, and economic independence.
Expansion of India Post Payment Bank: More than 100 new branches of the India Post Payment Bank will be established in the North East region. This expansion will facilitate greater financial inclusion, providing banking services to remote and underserved areas.
Polavaram Irrigation Project: The completion of the Polavaram Irrigation Project is prioritized to ensure food security. This project is expected to significantly boost agricultural productivity and provide a reliable water source to the farmers.
Job Creation in Manufacturing: To address unemployment, the government has introduced incentives for EPFO contributions. Additionally, a new scheme aims to skill 20 lakh youths, preparing them for employment in the manufacturing sector.
MSME Term Loans: A new credit guarantee scheme with up to ₹100 crore cover per applicant has been introduced for MSMEs. This initiative will provide much-needed financial support to small and medium enterprises, fostering entrepreneurship and innovation.
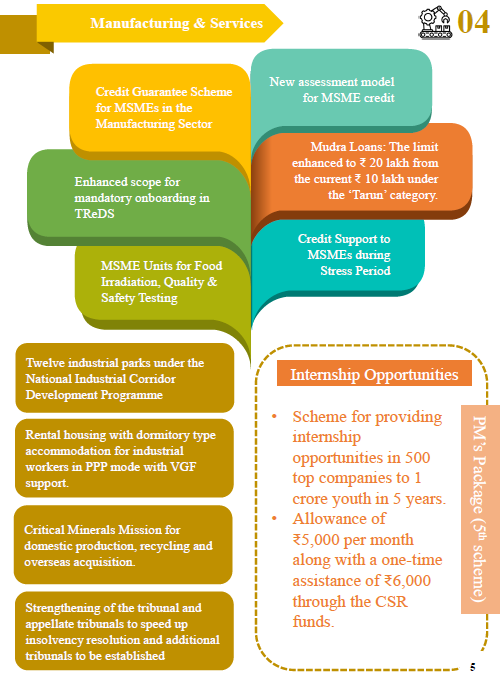
Power Projects: A new 2400 MW power project worth ₹21,400 crore has been announced. This project will enhance the country’s energy security and support sustainable economic growth.
Mudra Loans: The limit for Mudra Loans has been enhanced from ₹10 lakhs to ₹20 lakhs. This increase will enable more small businesses to access credit and expand their operations.
Rural Development: A substantial ₹2.66 lakh crore has been allocated for rural infrastructure development. This investment will improve the quality of life in rural areas by providing better roads, water supply, and sanitation facilities.
Agriculture and Allied Sectors: The budget allocates ₹1.52 lakh crore to the agriculture and allied sectors. This fund will support various agricultural initiatives, ensuring food security and boosting farmers’ incomes.
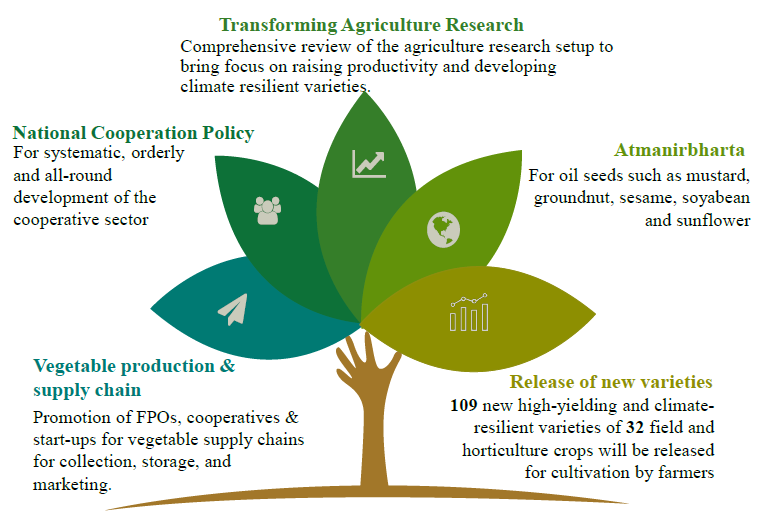
Affordable Housing: The government has announced 30 million additional houses under its affordable housing scheme. This initiative aims to provide homes to the urban poor, addressing the housing shortage issue in cities.
Nine Key Priorities
- Productivity and Resilience in Agriculture: Enhancing agricultural productivity through modern techniques and ensuring resilience against climate change.
- Employment and Skilling: Focusing on job creation and skill development to prepare the workforce for future challenges.
- Inclusive Human Resource Development and Social Justice: Promoting inclusive growth and social justice through various welfare schemes.
- Manufacturing Services: Boosting the manufacturing sector to create jobs and drive economic growth.
- Urban Development: Investing in the development of urban infrastructure and smart cities.
- Energy Security: Ensuring a reliable and sustainable energy supply to support economic activities.
- Infrastructure: Building robust infrastructure to facilitate trade and connectivity.
- Innovation and R&D: Promoting research and development to drive innovation and technological advancement.
- Next Generation Reforms: Implementing reforms to enhance efficiency and transparency in governance.
Changes in Personal Income Tax
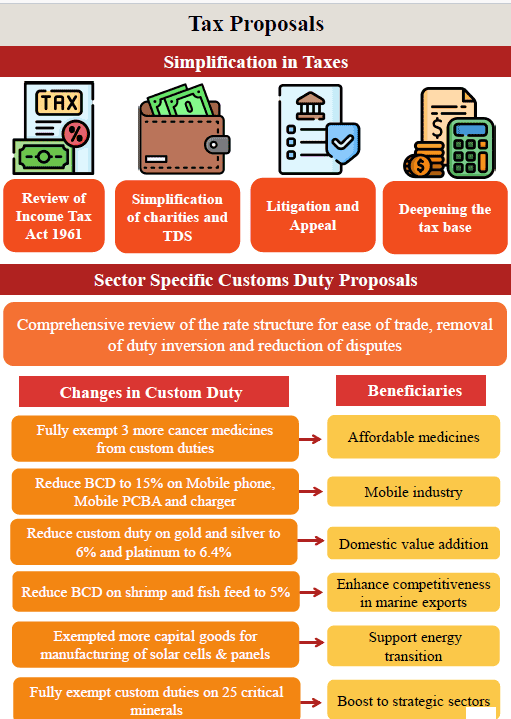
The budget also introduces significant changes in personal income tax to provide relief to taxpayers:
- Standard Deduction for Salaried Class: Increased from ₹50,000 to ₹75,000.
- Family Pension Deduction: Increased from ₹15,000 to ₹25,000.
New Income Tax Slabs:
- 0 – ₹3 lakh: Nil
- ₹3 lakh – ₹7 lakh: 5%
- ₹7 lakh – ₹10 lakh: 10%
- ₹10 lakh – ₹12 lakh: 15%
- ₹12 lakh – ₹15 lakh: 20%
- Above ₹15 lakh: 30%
Direct Tax Updates
- Comprehensive review of the Income Tax Act, 1961, to be completed in 6 months.
- Merging two tax exemption regimes for charities into one.
- Reduction of TDS rate on e-commerce operators from 1% to 0.1%.
- The credit of TCS to be given in the TDS to be deducted on salaries.
- Simplification and rationalization of reopening and reassessment processes.
- Simplification of compounding guidelines for TDS defaults.
- Rationalization of capital gains tax.
- Reduction of reassessment period in search cases from 10 years to 6 years.
- STCG on certain financial assets to attract 20% tax.
- LTCG on all financial and non-financial gains to be taxed at 12.5%.
- Listed financial assets held for more than 1 year to be classified as long-term.
- Increase in exemption limit on LTCG for certain assets to ₹1.25 lakh.
- Introduction of Vivaad se Vishwas Scheme 2024.
- Deployment of more officers to clear backlogs of first appeal.
- Expansion of “safe harbor” rules.
- Increase in monetary limits for filing appeals.
- Abolishment of angel tax for all classes of tax.
- They are streamlining the TP assessment procedure.
- The simpler tax regime for foreign shipping companies operating domestic cruises.
- Reduction of corporate tax on foreign companies from 40% to 35%.
- Increase in STT on F&O to 0.2% and 0.1%.
- Taxation of income from buyback.
- De-penalization of non-reporting of movable assets up to ₹20 lakh under IBC.
- Withdrawal of Equalisation Levy.
- The standard deduction for salaried employees increased from ₹50,000 to ₹75,000.
- Revision of tax structure under the new regime.
Engage with Us
What are your thoughts on the Union Budget 2024-25? Do you think the allocations and reforms will significantly impact India’s growth and development? Share your views in the comments below!
Stay tuned for more updates and in-depth analyses on the Union Budget 2024-25.





